Woodworking Accessories Tips
Why White Glue is Replacing Super Glue: A Look Through the History of Adhesives
In the world of custom furniture, woodworking, and home renovations, adhesives have always played a crucial role. With advancements in technology and a growing focus on environmental sustainability, Contact Cement is gradually being replaced by more eco-friendly and safer alternatives like white glue. Why is this shift happening? In this article, we’ll explore the history of adhesives, the reasons behind the decline of all-purpose adhesive, and how white glue is leading the future of adhesive technology.
A Brief History of Adhesives: From Natural Sources to Chemical Innovations
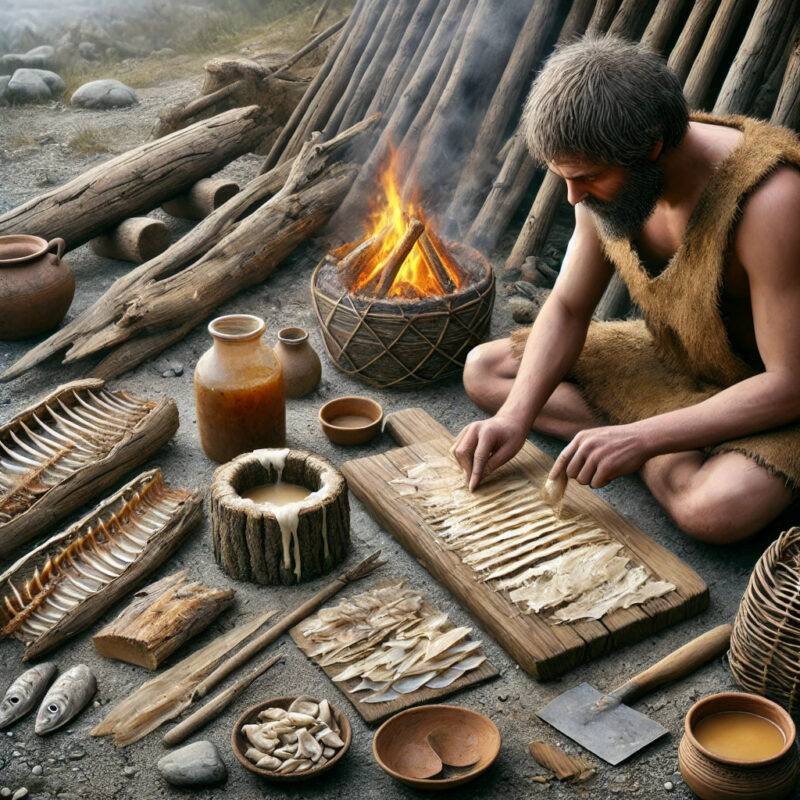
Adhesives have been used for thousands of years. Ancient civilizations used natural substances such as animal bones and fish scales to glue wood and pottery. With the rise of the industrial age, synthetic adhesives were developed. Among these, super glue (also known as contact cement or chloroprene adhesive) became extremely popular in the 20th century due to its versatility and strong bonding capabilities.
Super glue could bond various materials like wood, plastic, metal, glass, and more, making it indispensable in industries like construction, furniture making, and shoemaking.

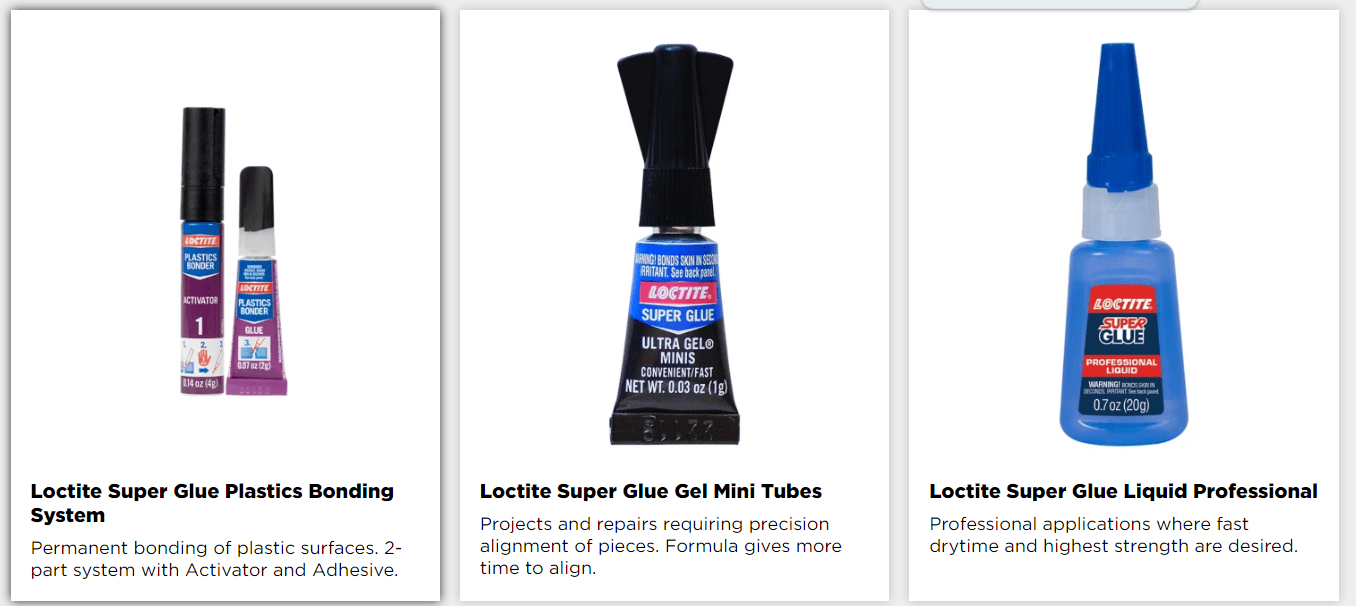
1.Versatility: As its name suggests, contact cementcan bond nearly any material. Its ability to work with multiple surfaces made it the go-to adhesive in many industries.
2.Quick Drying: One of the key benefits of all-purpose adhesive is its fast curing time. It solidifies within minutes, enhancing production efficiency.
3.Strong Bond: Super glue provides an extremely strong hold, capable of withstanding significant loads. This made it ideal for use in applications requiring durable, high-strength bonds.
However, over time, as environmental and health concerns grew, super glue’s downsides became more apparent, especially in industries like furniture making, where white glue began to offer a safer and more sustainable alternative.

Environmental Concerns
Super glue contains large amounts of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are released into the air as it dries. These compounds are harmful to the environment and can pose health risks to humans, especially with prolonged exposure. Over time, global regulations concerning air quality and the emission of toxic substances have become stricter, driving industries to seek eco-friendly alternatives.
White glue made primarily of polyvinyl acetate (PVA)—emerged as a leading substitute. Unlike super glue, white glue does not release harmful fumes, making it a safer option for both manufacturers and end-users.
The Environmental Benefits of White Glue
White glue is water-based, with its primary ingredient being polyvinyl acetate. This makes it not only safer for the environment but also less hazardous to human health. Its eco-friendly properties include:
Non-toxic and odorless: White glue is free of harmful chemicals and does not emit strong, harmful odors during application or drying. This makes it especially suitable for indoor use and in applications where air quality is crucial, such as children’s furniture.
Easy to clean: Because it is water-based, white glue can be easily cleaned with water before it dries, unlike super glue, which can be challenging to remove once applied.
Health & Safety Requirements
In today’s world, consumers are becoming increasingly concerned about indoor air quality and the overall safety of household products. White glue, with its non-toxic properties and minimal VOC emission, is seen as a much safer alternative to super glue. In regions with strict environmental standards, such as Europe and North America, PVA glue is quickly becoming the adhesive of choice for furniture manufacturers and interior decorators.
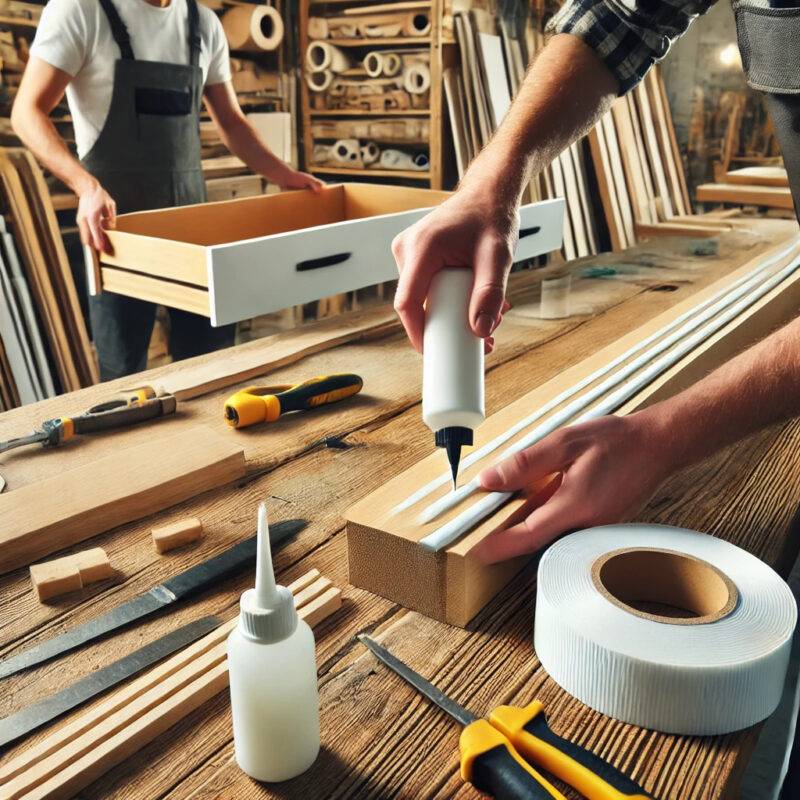

White Glue’s Applications and Benefits
1.While white glue is primarily used for bonding wood and paper, recent advancements have expanded its capabilities. It’s now widely used in custom furniture making, flooring, and woodworking, replacing super glue in many areas.
2.Furniture production: White glue is widely applied in wooden furniture assembly, edge-banding, and veneering, offering sufficient bonding strength and superior environmental performance.
3.Interior decoration: In applications involving lightweight materials like fabric, wallpaper, and wood veneers, white glue delivers excellent results without the health risks associated with super glue.
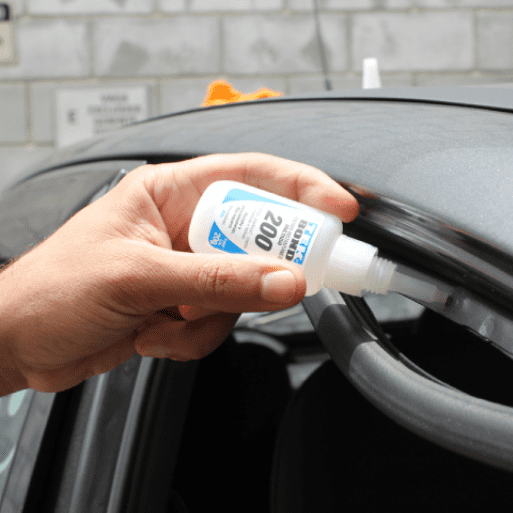

The Current Status of Super Glue Still in Use for Specific Needs
Despite the growing popularity of white glue, super glue remains relevant in certain areas. For example, when bonding dissimilar materials (such as metal and plastic), super glue’s superior strength and versatility make it irreplaceable. Additionally, in industries requiring strong, immediate bonds—such as automotive and construction—super glue still plays a vital role.
Looking Ahead: The Rise of Green Adhesives
As technology continues to evolve and regulations around environmental sustainability tighten, the adhesive industry is shifting toward green, eco-friendly, and safe solutions. White glue is just one of many eco-friendly adhesives currently on the market, but its success signals a broader trend toward reducing environmental impact and improving indoor air quality. In the future, more adhesives will likely be developed to meet both industrial needs and global sustainability standards.

Conclusion
The gradual replacement of super glue by white glue is primarily driven by the increasing demand for environmentally friendly and health-conscious products. As more manufacturers and consumers prioritize safety and sustainability, white glue—with its non-toxic, odorless, and eco-friendly properties—has emerged as the preferred adhesive in the furniture and home renovation industries.
While super glue still has its place in specific applications, the trend is clear: the future of adhesives lies in sustainability, and PVA-based white glue is leading the charge.





